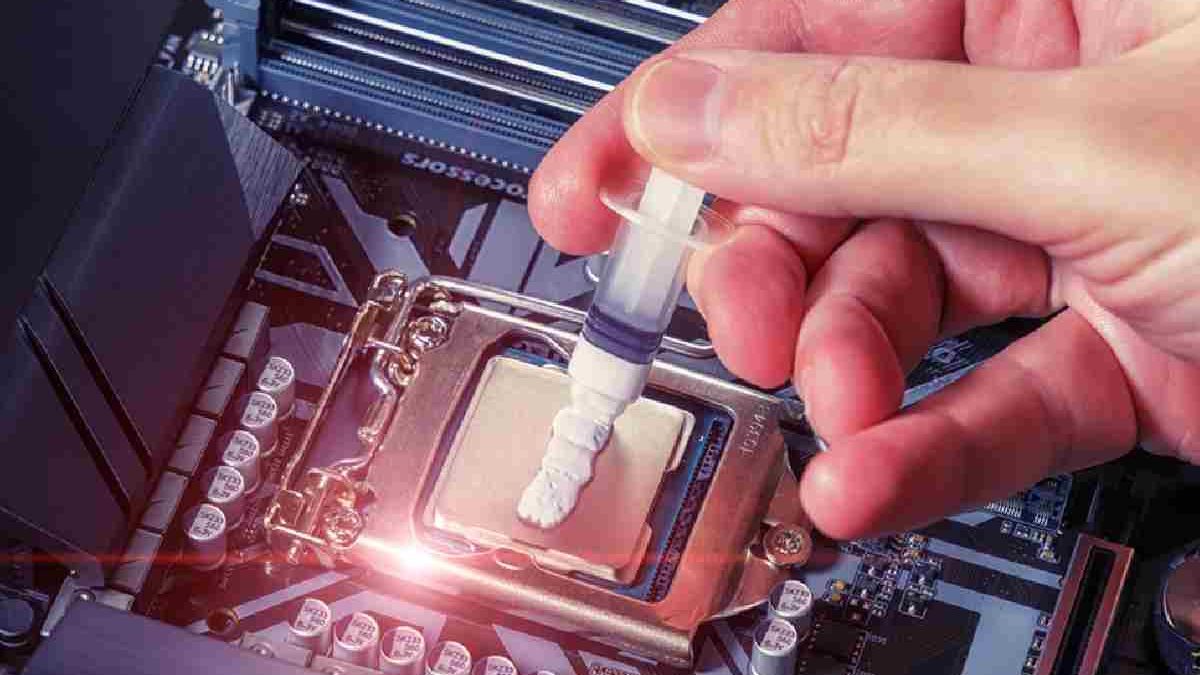
Want to get the most out of your CPU? Applying thermal paste correctly can significantly improve your system’s cooling efficiency. Understanding the best thermal paste patterns ensures you keep your processor running smoothly and efficiently.
For those wondering how to apply thermal paste, there are several effective patterns: the dot method for simplicity and even spread, the line method for rectangular CPUs, the X method for larger processors, and the spread method for guaranteed coverage. Each pattern has its own advantages, making it important to choose the right one for your specific use case and cooling setup.
Let’s take a closer look at everything thermal paste — from why it’s important to the best application methods for your build.
Table of Contents
Starting with the Basics: What Is Thermal Paste?
Thermal paste is a thermally conductive material used to enhance the heat transfer between two surfaces. It is typically applied between a heat-generating component and a heat sink. The primary function of thermal paste is to fill microscopic air gaps and imperfections on the surfaces of these components, ensuring efficient thermal conductivity.
Top Thermal Paste Application Methods and Their Ideal Uses
Choosing the right pattern and applying the correct amount of thermal paste is necessary for maintaining optimal thermal performance and ensuring the longevity of computer components. The pattern used to apply thermal paste can impact its effectiveness. Here are some common patterns and their best use cases:
Dot Method:
- Description: A small, pea-sized dot in the center of the processor.
- Best for: Simplicity and general use, especially for smaller CPUs.
- Pros: Minimizes risk of excess paste.
- Cons: May not cover the corners of larger processors.
X Method:
- Description: An X shape across the CPU surface.
- Best for: Larger processors that need more comprehensive coverage.
- Pros: Ensures better coverage.
- Cons: Harder to control the amount of paste, risk of excess.
Line Method:
- Description: A straight line down the center of the CPU.
- Best for: Rectangular processors.
- Pros: Good for elongated CPUs.
- Cons: May not cover corners of square processors.
Buttered Toast Method:
- Description: Spreading the paste evenly across the surface.
- Best for: Users who can control the volume of paste.
- Pros: Ensures even coverage.
- Cons: Requires skill to avoid excess paste.
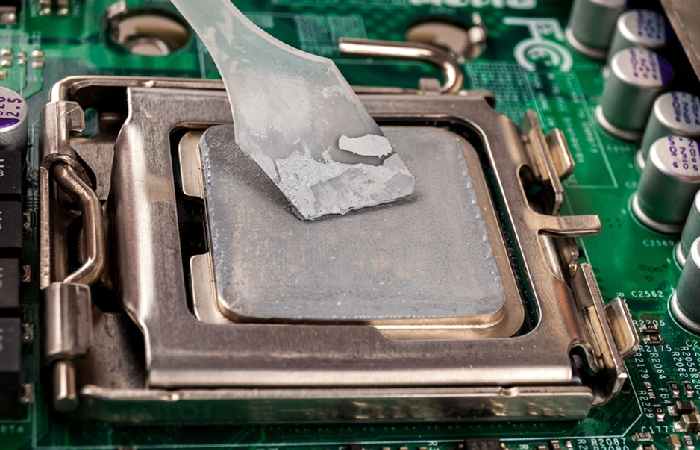

What Happens if Thermal Paste Is Not Applied Correctly?
Incorrect application of thermal paste can lead to several issues, including:
Insufficient Coverage:
- Issue: Not applying enough paste leads to inadequate heat transfer, risking overheating.
- Solution: Use a syringe or tube for precise application, targeting a pea-sized amount for the dot method or appropriately adjusted amounts for other processor shapes. Utilize a non-conductive tool to slightly spread the paste at the center before applying the cooler to help ensure complete coverage without overflow.
Excessive Application:
- Issue: Over-application can cause the paste to spill over, risking short circuits, especially with conductive pastes.
- Solution: Start with a small amount and increase incrementally if needed. After application, gently press the heat sink onto the paste to check if it spreads without spilling over the processor edges.
Uneven Distribution:
- Issue: Poor application technique can lead to air pockets, reducing efficiency and creating hot spots.
- Solution: After applying the paste, carefully lower the cooler directly down onto the center of the processor to avoid shifting the paste unevenly. Consider using a non-abrasive tool like a plastic spatula to gently smooth out the paste for methods like the spread technique, ensuring a thin, even layer across the surface.
How Often Should Thermal Paste Be Replaced?
Thermal paste degrades over time due to the heat generated by the CPU, which dries out the solvent in the paste. This degradation reduces its thermal transfer efficiency. The frequency of replacement depends on several factors:
- Usage Intensity: High-demand usage may require more frequent replacement.
- Quality of Paste: Higher quality pastes last longer.
- General Recommendation: Replace every one to two years, but monitor processor temperatures and the physical condition of the paste for more accurate timing.
Why Do People Use Thermal Paste for Computers?
Thermal paste is great for computer thermal management. It enhances heat transfer between heat-generating components and heat sinks. Its ability to fill air gaps, conform to irregular surfaces, and provide consistent thermal conductivity makes it an essential material for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and ensuring the longevity and performance of computer components.
Improved Heat Transfer:
- Filling Air Gaps: Thermal paste fills the tiny air gaps and imperfections between the CPU and the heat sink, which would otherwise act as insulators and impede heat transfer. This ensures that heat is efficiently transferred from the component to the heat sink, preventing overheating.
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity: The paste provides a thin, uniform layer that enhances thermal conductivity, allowing for better cooling performance in conjunction with components like CPU coolers. This is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, especially during high-performance tasks like gaming or overclocking.
Application Flexibility:
- Conformity to Irregular Surfaces: Being a liquid, thermal paste can conform to irregular surfaces better than thermal pads, ensuring consistent contact and heat transfer across the entire surface area.
- Automation Capabilities: Thermal paste can be applied using automated dispensers, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing processes where consistency and precision are required.
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Lower Cost: Compared to thermal pads, thermal paste is generally less expensive, making it a cost-effective solution for thermal management in computers.
- Minimal Material Usage: Only a small amount of thermal paste is needed to achieve effective heat transfer, which further reduces costs.
Durability and Stability:
- Long-Term Stability: High-quality thermal pastes are designed to remain stable over time, even under intense thermal cycling and vibrations, which is essential for the longevity of computer components.
- Low Outgassing: Some thermal pastes are formulated to meet low outgassing standards, ensuring that they do not release volatile compounds that could damage sensitive components like cameras or optical equipment.

Securing System Longevity with Proper Thermal Paste Application
Selecting the right thermal paste pattern will help you maximize the cooling efficiency and performance of your CPU. By understanding and applying the correct amount and method, you ensure optimal heat transfer and prolong the life of your components. As thermal management technology advances, staying updated on new techniques can further enhance your system’s effectiveness. Embrace these practices to maintain a cool, efficient, and high-performing computer system.